Key Takeaways
Before diving into the details, here are some quick insights:
- The x and y axis are fundamental components of the Cartesian coordinate system.
- They are used in various fields such as mathematics, physics, engineering, and data visualization.
- Understanding how to plot and interpret these axes is crucial for analyzing graphs and charts.
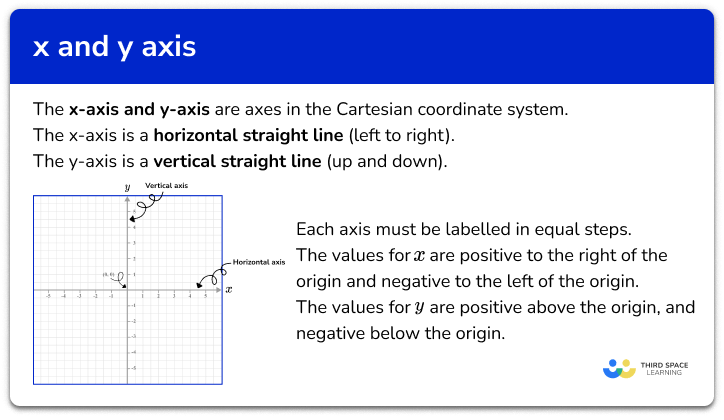
The Basics of the Cartesian Coordinate System
The Cartesian coordinate system is a two-dimensional plane defined by two perpendicular lines: the x-axis and the y-axis. Named after the French mathematician René Descartes, this system provides a method for identifying the position of points in a plane through ordered pairs of numbers.
The X Axis
The x-axis is the horizontal line in the Cartesian coordinate system. It typically represents the independent variable in a graph or chart. The values on the x-axis can be positive or negative, extending infinitely in both directions. This axis is crucial for plotting data points and understanding the relationship between variables.
The Y Axis
Perpendicular to the x-axis, the y-axis is the vertical line in the Cartesian coordinate system. It usually represents the dependent variable, which changes in response to the independent variable. Like the x-axis, the y-axis also extends infinitely in both directions, accommodating both positive and negative values.
Applications of the X and Y Axis
The x and y axis are not just theoretical concepts but have practical applications in various fields:
Mathematics
In mathematics, the x and y axis are used extensively to graph equations and inequalities. They help in visualizing functions, solving systems of equations, and understanding geometric shapes. For instance, plotting a linear equation on the x and y axis allows for the visualization of its slope and intercept.
Physics
In physics, these axes are essential for plotting motion, velocity, and acceleration graphs. They help in understanding the relationship between different physical quantities and predicting future trends. For example, a velocity-time graph uses the x-axis to represent time and the y-axis to represent velocity.

Engineering
Engineers use the x and y axis to design and analyze mechanical systems. Whether it’s plotting stress-strain curves or analyzing electrical circuits, these axes provide a framework for understanding complex systems and making informed decisions.
Data Visualization
In the world of data visualization, the x and y axis are used to create bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, and more. They enable data analysts to present information clearly and concisely, making it easier for stakeholders to grasp insights and make data-driven decisions.
How to Plot Points on the X and Y Axis
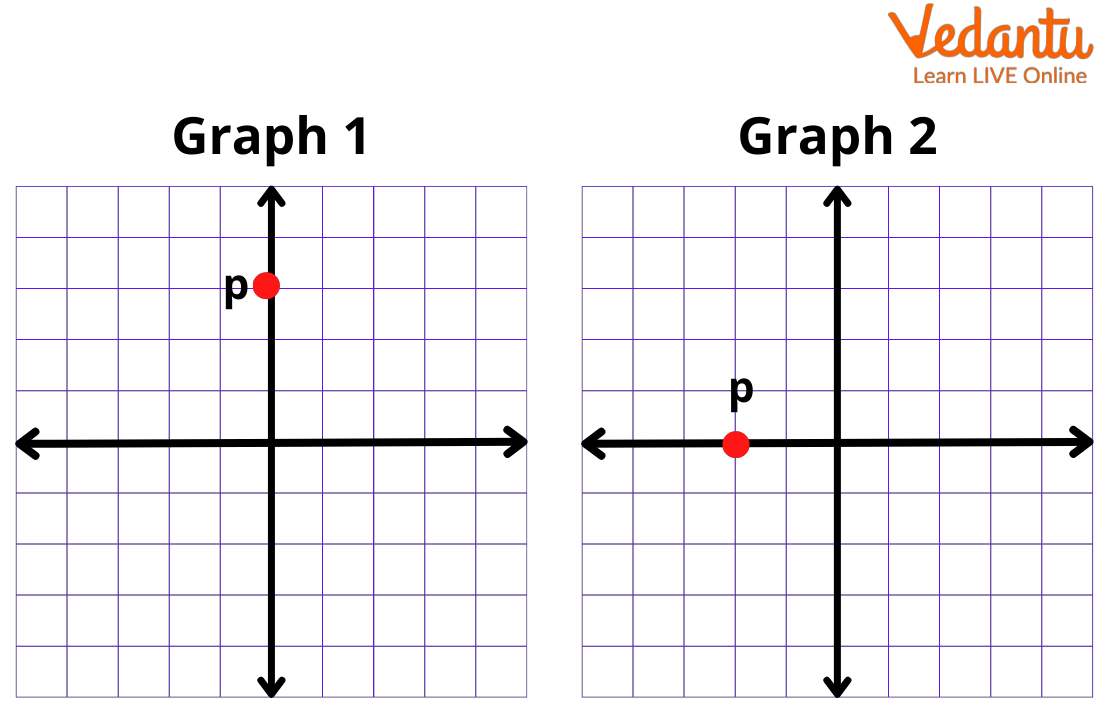
Plotting points on the x and y axis is a fundamental skill in graphing. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the coordinates of the point, typically written as (x, y).
- Locate the x-coordinate on the x-axis.
- From the x-coordinate, move vertically to the y-coordinate on the y-axis.
- Mark the point where these two values intersect.
This process allows for the accurate representation of data points on a graph, facilitating analysis and interpretation.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When working with the x and y axis, several common mistakes can occur:
Confusing the Axes
A frequent error is mixing up the x and y axes. Remember, the x-axis is horizontal, and the y-axis is vertical. A simple mnemonic is that “x” rhymes with “axis,” emphasizing its horizontal nature.

Mislabeling Data
Incorrectly labeling data on the axes can lead to misinterpretation. Always double-check that the data corresponds to the correct axis and is accurately labeled.
Ignoring Units
Units are crucial for understanding the scale and meaning of a graph. Ensure that both axes are clearly labeled with the appropriate units to convey accurate information.
Advanced Concepts: Beyond the Basics
Once you have a firm grasp of the x and y axis, you can explore more advanced concepts:
3D Coordinate Systems
In three-dimensional space, a third axis, the z-axis, is introduced. This axis is perpendicular to both the x and y axes, allowing for the representation of three-dimensional objects and relationships.
Polar Coordinates
Polar coordinates offer an alternative to the Cartesian system, using a radius and angle to locate points. This system is particularly useful in fields like astronomy and engineering, where circular or rotational motion is involved.
The x and y axis are foundational elements of the Cartesian coordinate system, playing a crucial role in various fields such as mathematics, physics, engineering, and data visualization. Understanding how to use these axes effectively is essential for analyzing graphs, interpreting data, and solving complex problems. By mastering the x and y axis, you can unlock a deeper understanding of the world around you and enhance your analytical skills.